Mastering Process Groups and Knowledge Areas in the PMBOK® Guide 7th Edition
Overview of the PMBOK® Guide 7th Edition
The PMBOK® Guide (Project Management Body of Knowledge) 7th Edition is the most current and comprehensive resource for project management professionals seeking to enhance their understanding of project processes and best practices. Developed by the Project Management Institute (PMI)®, this guide provides essential frameworks, methodologies, and standards that help project managers successfully execute projects across various industries. It also includes a process group and knowledge table and other key resources for preparing for your PMP Exam.
One of the most critical aspects of the PMBOK® Guide is the classification of Process Groups and Knowledge Areas. These two structures form the foundation of project management, helping professionals systematically plan, execute, and close projects while ensuring alignment with organizational goals. Mastering the process group and knowledge table is essential for anyone preparing for the Project Management Professional (PMP)® exam, as it offers a structured way to understand how different project management elements interact.
Importance of Understanding Process Groups and Knowledge Areas
Project management is a structured discipline that requires a clear understanding of its core components. Process Groups represent the high-level stages of managing a project, while Knowledge Areas categorize the essential skill sets and methodologies needed for successful execution. The interplay between these two concepts is visually captured in the process group and knowledge table, which serves as a quick reference guide for project managers and PMP exam candidates alike.
Key Benefits of Mastering Process Groups and Knowledge Areas:
- Systematic Project Execution: Helps managers approach projects in a structured manner, ensuring that each phase is completed efficiently.
- Improved Decision-Making: Enhances the ability to make informed decisions by providing a framework for evaluating project progress.
- Better Risk Management: Facilitates proactive identification and mitigation of risks, reducing project failures.
- Enhanced Communication: Ensures that project stakeholders have a clear understanding of roles, responsibilities, and expectations.
- Essential for PMP Exam Success: A deep understanding of these concepts is crucial for passing the PMP exam, which heavily tests knowledge of Process Groups and Knowledge Areas.
How Mastering These Concepts Enhances Project Success
The ability to manage projects efficiently is directly tied to how well one understands the Process Groups and Knowledge Areas. These classifications serve as a universal project management language, ensuring that professionals across different industries and organizations follow a common standard.
Consider a scenario where a project manager needs to develop a new product within a tight deadline. By leveraging the Process Groups, they can systematically initiate, plan, execute, monitor, and close the project while ensuring adherence to best practices within relevant Knowledge Areas such as scope management, schedule management, and quality control.
For instance, understanding the schedule knowledge area PMBOK Guide is critical when developing project timelines and dependencies. This ensures that teams stay on track, avoid unnecessary delays, and optimize resource allocation. Similarly, by referring to the process group and knowledge table, project managers can quickly identify which processes are applicable at each stage of the project lifecycle.
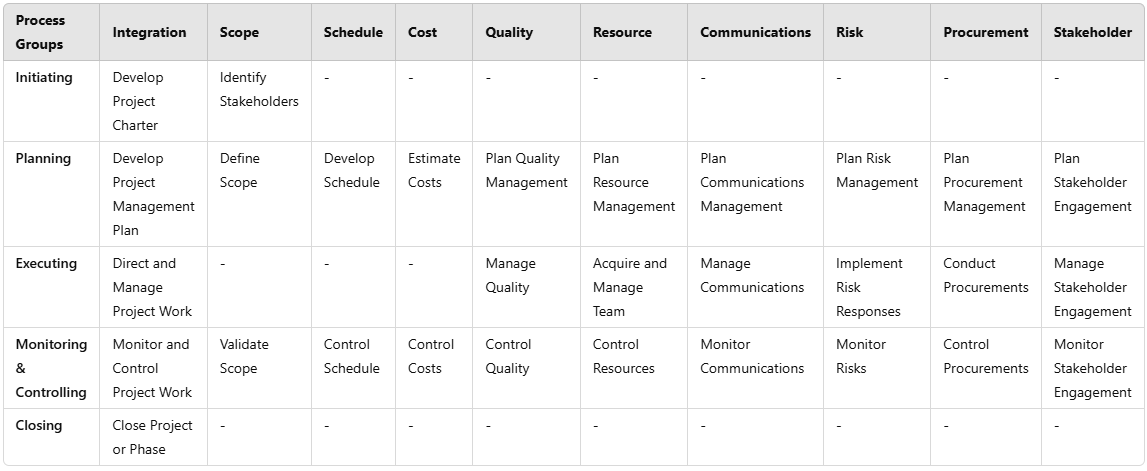
The Process Group and Knowledge Table: A Key Reference
The process group and knowledge table is an invaluable tool that visually maps the interactions between the Process Groups and Knowledge Areas. This table serves as a quick reference guide for PMP candidates and project managers who need to apply PMBOK principles in real-world scenarios.
Below is an example of how Process Groups and Knowledge Areas align:
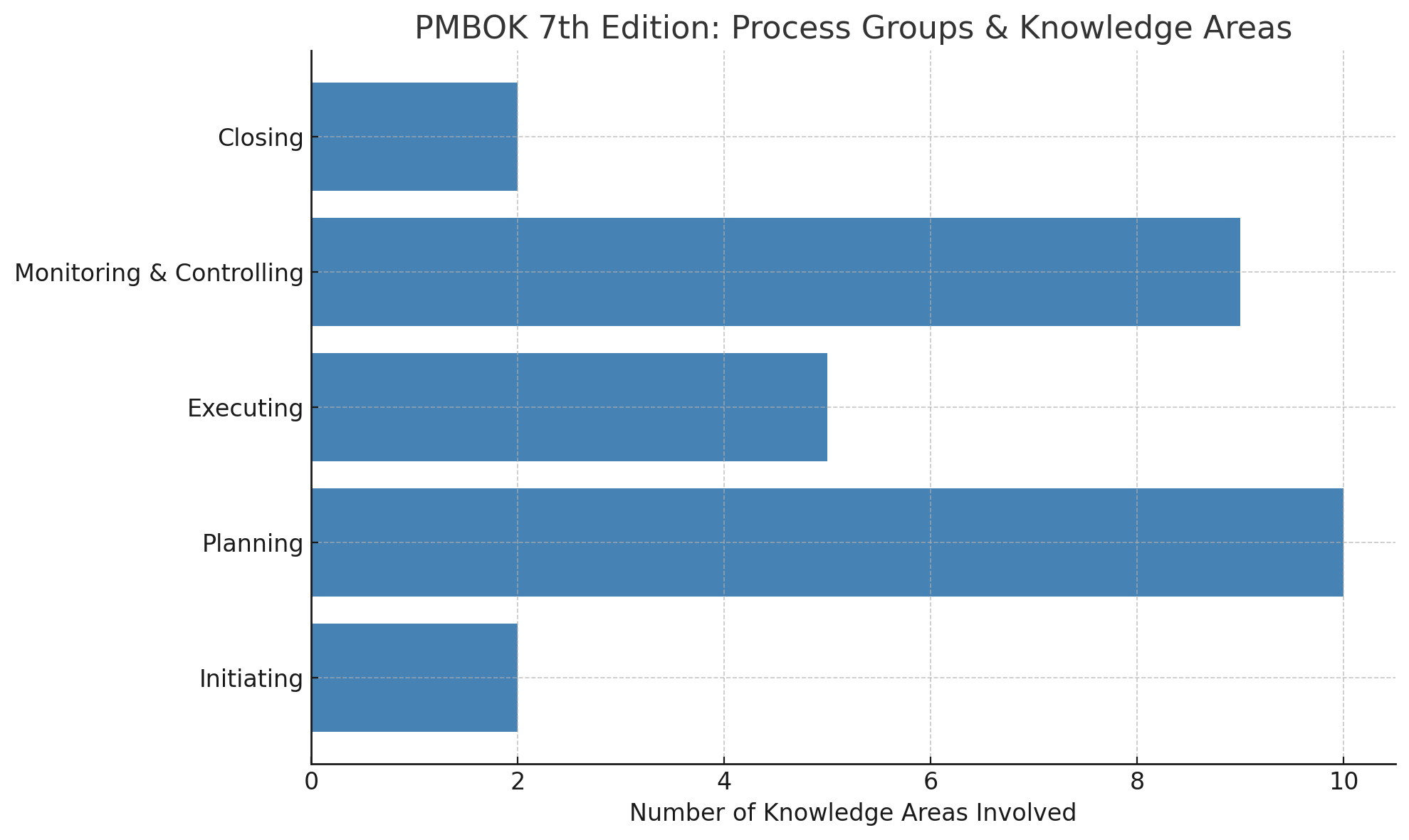
The Five PMBOK® Guide Process Groups
The PMBOK® Guide defines five Process Groups, which represent the fundamental phases of a project. These Process Groups help organize project activities systematically, ensuring efficient project execution from start to finish.
1. Initiating Process Group
The Initiating Process Group marks the beginning of a project. It defines the high-level scope, objectives, and key stakeholders. The primary goal is to gain authorization for the project and ensure alignment with business objectives.
Key Processes in the Initiating Process Group:
- Develop Project Charter: Officially authorizes the project and outlines objectives.
- Identify Stakeholders: Recognizes individuals and groups impacted by the project.
2. Planning Process Group
The Planning Process Group establishes the roadmap for the project. This stage involves defining the scope, objectives, timelines, and required resources. Effective planning sets the foundation for successful execution and reduces uncertainty.
Key Processes in the Planning Process Group:
- Develop Project Management Plan: Creates a comprehensive plan that integrates all project components.
- Define Scope: Outlines project deliverables and requirements.
- Develop Schedule: Establishes timelines and milestones.
- Estimate Costs & Plan Budget: Allocates financial resources effectively.
- Plan Risk Management: Identifies potential project risks and mitigation strategies.
3. Executing Process Group
The Executing Process Group focuses on implementing the project plan. This phase involves coordinating resources, managing stakeholder expectations, and ensuring project objectives are met.
Key Processes in the Executing Process Group:
- Direct and Manage Project Work: Oversees project execution and ensures deliverables are completed.
- Manage Quality: Implements quality standards and processes.
- Acquire and Manage Team: Ensures appropriate staffing and team performance.
- Manage Communications: Facilitates effective information flow among stakeholders.
4. Monitoring & Controlling Process Group
The Monitoring & Controlling Process Group ensures project performance aligns with the planned scope, schedule, and budget. It involves tracking progress, identifying variances, and taking corrective actions when necessary.
Key Processes in the Monitoring & Controlling Process Group:
- Monitor and Control Project Work: Assesses project performance against objectives.
- Validate Scope & Control Changes: Ensures deliverables meet requirements.
- Control Schedule & Costs: Manages deviations from the project plan.
- Monitor Risks: Identifies and mitigates risks proactively.
5. Closing Process Group
The Closing Process Group finalizes all project activities and ensures all deliverables are completed as planned.
Key Processes in the Closing Process Group:
- Close Project or Phase: Formally concludes the project and archives documents.
- Lessons Learned: Captures insights for future projects.
The 10 PMBOK® Guide Knowledge Areas
The PMBOK® Guide organizes project management processes into ten Knowledge Areas, each representing a critical aspect of managing a project. These Knowledge Areas provide project managers with a structured way to approach project planning, execution, and control.
Overview of Each Knowledge Area and Real-World Application
- Project Integration Management – Ensures all project elements work together effectively.
- Example: Developing a project charter to define project scope and objectives.
- Project Scope Management – Defines what is included in the project and prevents scope creep.
- Example: Creating a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to outline deliverables.
- Project Schedule Management – Manages the project’s timeline and ensures deadlines are met.
- Example: Developing a project schedule using the Critical Path Method (CPM).
- Project Cost Management – Estimates and controls project costs to stay within budget.
- Example: Performing cost variance analysis to track spending.
- Project Quality Management – Ensures project deliverables meet quality standards.
- Example: Conducting quality audits to verify compliance with project requirements.
- Project Resource Management – Manages team members and physical resources.
- Example: Assigning roles and responsibilities through a Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM).
- Project Communications Management – Ensures clear and effective information flow.
- Example: Using a communication plan to keep stakeholders informed.
- Project Risk Management – Identifies and mitigates potential project risks.
- Example: Conducting a risk assessment and developing mitigation strategies.
- Project Procurement Management – Handles contracts and acquisitions of goods and services.
- Example: Negotiating vendor contracts for outsourced work.
- Project Stakeholder Management – Engages and manages stakeholder expectations.
- Example: Holding stakeholder meetings to address concerns and gather feedback.
Each of these Knowledge Areas plays a critical role in ensuring project success by addressing specific challenges that project managers face. Understanding how they integrate with the Process Groups is key to mastering project management principles and excelling in the PMP® exam.
The Relationship Between Process Groups and Knowledge Areas
Understanding the relationship between Process Groups and Knowledge Areas is crucial for effective project management. These two frameworks intersect in a way that ensures every aspect of project management is systematically addressed.
How Process Groups Integrate with Knowledge Areas
Each Knowledge Area contains specific project management processes that align with different Process Groups. This integration ensures that project activities are planned, executed, and monitored effectively. For example:
- Project Scope Management is primarily associated with the Planning Process Group, where scope definition, validation, and control occur.
- Project Risk Management spans multiple Process Groups, with risk identification occurring in Planning, risk response implementation in Executing, and risk monitoring in Monitoring & Controlling.
- Project Procurement Management involves planning procurement strategies, selecting vendors in Executing, and closing procurement contracts in the Closing Process Group.
This interconnected framework ensures that projects follow a structured lifecycle while addressing the specific needs of each Knowledge Area.
Explanation of the Process Group and Knowledge Table
The process group and knowledge table is a critical reference tool for PMP candidates and project managers. This table visually represents the relationships between Process Groups and Knowledge Areas, helping professionals quickly understand where each process fits within the broader project management framework. By using this table, project managers can:
- Identify which Knowledge Areas are most relevant at each phase of the project.
- Ensure that all required project management processes are completed within their respective Process Groups.
- Prepare effectively for the PMP exam by understanding how different processes interact.
Common Misconceptions and How to Avoid Them
Despite its structured approach, some common misconceptions arise when studying the relationship between Process Groups and Knowledge Areas:
- Process Groups are NOT the same as project phases – While Process Groups occur in every phase of a project, they do not define specific project lifecycle stages (e.g., initiation, design, execution).
- Each Knowledge Area spans multiple Process Groups – No Knowledge Area is limited to just one Process Group; instead, processes within each area are distributed across multiple groups.
- The process group and knowledge table is not static – Depending on the project, some processes may be emphasized more than others, requiring flexibility in application.
By understanding these relationships and avoiding common misconceptions, project managers can better navigate the complexities of real-world projects and effectively prepare for the PMP exam.
Process Groups and Knowledge Areas Table
A deeper understanding of the process group and knowledge table is crucial for project managers and PMP candidates. This table visually aligns project management Process Groups with corresponding Knowledge Areas, allowing professionals to see where specific processes fit into the overall project framework.
How to Interpret the Process Group and Knowledge Table
The process group and knowledge table is structured to ensure that project managers can easily reference which Knowledge Areas apply at each stage of a project. Each cell in the table represents a distinct process that integrates a specific Process Group and Knowledge Area. By studying this table, project managers can:
- Identify key activities required at different stages of a project.
- Ensure all necessary project management processes are accounted for.
- Improve their ability to answer PMP exam questions related to process interactions.
Understanding the process group and knowledge table is not just beneficial for exam preparation but also for applying project management methodologies effectively in real-world scenarios. For example, Project Risk Management involves risk identification during the Planning Process Group, while risk monitoring continues in the Monitoring & Controlling Process Group. This structured view helps project managers track project health and adjust plans proactively.
Best Practices for Using the Process Group and Knowledge Table
- Memorization for Exam Success: Given its importance, PMP candidates should memorize the table to quickly recall how Process Groups and Knowledge Areas interact.
- Application in Project Management: In day-to-day project work, the table can be used as a checklist to ensure that no critical process is overlooked.
- Common Pitfalls to Avoid: One common mistake is assuming that Process Groups align perfectly with project phases. In reality, all Process Groups can occur multiple times throughout the project lifecycle.
By leveraging the process group and knowledge table, project managers can ensure they follow best practices while also preparing effectively for the PMP exam.
How to Use the Process Group and Knowledge Table for PMP Exam Preparation
The process group and knowledge table is one of the most valuable resources for PMP exam candidates. Understanding how to effectively utilize this table can significantly improve exam performance and comprehension of project management processes.
Best Practices for Memorization and Application
- Break It Down: Instead of memorizing the entire table at once, study each Process Group separately and then understand how it interacts with each Knowledge Area.
- Use Flashcards: Creating flashcards for each process and its respective group and area can reinforce memory retention.
- Practice with Real Scenarios: Apply each process to real-world project examples to solidify understanding.
- Recreate the Table from Memory: Regularly attempt to write out the process group and knowledge table without looking, then check for accuracy.
- Engage in PMP Exam Simulations: Use exam simulators that require knowledge of the table to practice answering complex questions correctly.
How Understanding This Structure Aids in Answering PMP Exam Questions
PMP exam questions often require candidates to analyze situations and determine which process is taking place within the project lifecycle. Having a firm grasp of the process group and knowledge table allows candidates to:
- Quickly identify which Process Group a given scenario falls under.
- Determine which Knowledge Area is relevant based on the context of the question.
- Select the correct answer with confidence by understanding the process interactions.
For example, if a question describes a project manager evaluating project performance, this would likely fall under Monitoring & Controlling and relate to processes like Monitor and Control Project Work or Validate Scope.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Overlooking Interdependencies: Many PMP candidates assume that each Knowledge Area functions in isolation. In reality, multiple areas overlap within the same Process Group.
- Confusing Process Groups with Phases: The Process Groups do not necessarily represent the sequential phases of a project. Instead, they repeat across various project phases.
- Ignoring Lesser-Known Processes: While core processes like Develop Project Charter and Develop Project Management Plan are well-known, other processes such as Control Resources or Monitor Communications are equally important.
- Neglecting Exam Simulation Practice: Memorization alone will not suffice. PMP candidates should consistently apply their knowledge in timed mock exams.
By following these best practices and avoiding common pitfalls, PMP candidates can maximize their chances of success on the exam while also improving their practical project management skills.
Visual Aids and Infographics
Understanding project management concepts can be greatly enhanced with the use of visual aids and infographics. These tools provide a simplified yet comprehensive way to represent complex interactions between Process Groups and Knowledge Areas, making it easier to grasp the relationships and dependencies among different project processes.
How Visual Representation Enhances Retention and Learning
- Cognitive Retention: Studies show that people remember visual content better than text. Diagrams, flowcharts, and tables help project managers recall information more quickly, especially when preparing for the PMP exam.
- Improved Understanding: Infographics break down complex topics, ensuring that even beginners can grasp project management frameworks without getting overwhelmed by jargon-heavy text.
- Quick Reference Tool: A well-designed process group and knowledge table infographic allows project managers to refer back to essential concepts during project execution, reducing errors and ensuring best practices are followed.
Recommended Visuals for PMP Exam Preparation
- Flowcharts: Illustrate how different Process Groups interact throughout a project lifecycle.
- Process Group Breakdown Diagrams: Show the key activities within each Process Group.
- Knowledge Area Maps: Highlight how Knowledge Areas intersect with different Process Groups.
- Risk Management Matrices: Provide a visual representation of risk categories and mitigation strategies.
- Stakeholder Influence Charts: Show how stakeholder engagement changes across project phases.
Best Practices for Using Infographics in Study Materials
- Print and Display: Keeping a process group and knowledge table infographic on a desk or wall makes it easy to glance at during study sessions.
- Use Color-Coding: Associating each Process Group with a unique color improves recognition and recall.
- Incorporate into Notes: PMP candidates can enhance their notes by adding diagrams that visually represent key concepts.
- Use Online Interactive Tools: Many project management tools provide interactive visuals that allow professionals to see dynamic connections between Process Groups and Knowledge Areas.
By incorporating visual aids and infographics, project managers can accelerate their understanding of the PMBOK® Guide, enhance their PMP exam preparation, and apply project management best practices more effectively in real-world scenarios.
Practical Application in Project Management
While understanding the Process Groups and Knowledge Areas is essential for passing the PMP exam, their true value lies in their real-world application. Project managers must seamlessly integrate these frameworks into their workflows to enhance project efficiency and effectiveness.
How to Use Process Groups and Knowledge Areas in Real-World Projects
- Aligning with Project Goals
- Before initiating a project, ensure that objectives align with organizational strategy.
- Use Project Integration Management to develop a charter that secures stakeholder buy-in.
- Ensuring Scope Control
- Clearly define project scope early in the Planning Process Group to avoid scope creep.
- Use Scope Management techniques like the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to prevent unnecessary work from being added mid-project.
- Managing Schedules and Resources
- Apply Schedule Management principles to create accurate timelines and manage dependencies.
- Ensure efficient resource allocation using Resource Management techniques.
- Risk and Quality Control
- Identify risks proactively using Risk Management tools such as risk registers.
- Implement quality control measures to ensure deliverables meet stakeholder expectations.
Aligning Project Workflows with PMBOK® Guide 7th Edition Principles
Modern project management tools incorporate PMBOK® principles, allowing teams to automate and streamline workflows.
- Agile and Hybrid Approaches: The PMBOK® Guide 7th Edition integrates adaptive project methodologies, helping managers choose between traditional (waterfall) and Agile frameworks.
- Software Integration: Many project management platforms (e.g., Microsoft Project, Trello, Asana) allow for PMBOK®-based workflow customizations.
- Continuous Improvement: Organizations use PMBOK® principles to refine project processes, ensuring long-term success and sustainability.
Tips for Integrating These Concepts into Project Planning Software
- Use Templates – Many project management tools offer pre-built PMBOK® templates to streamline project setup.
- Automate Reporting – Set up dashboards that monitor project performance in real time.
- Facilitate Collaboration – Use communication tools that align with PMBOK®’s Communications Management framework to keep stakeholders engaged.
By applying the Process Groups and Knowledge Areas in real-world projects, project managers can improve efficiency, reduce risk, and enhance stakeholder satisfaction.
Additional Study Resources and Tools
A well-structured study plan is crucial for mastering the PMBOK® Guide and successfully passing the PMP exam. Several resources and tools can help candidates reinforce their understanding of Process Groups and Knowledge Areas, improve retention, and gain hands-on experience with project management concepts.
Recommended PMP Study Guides and Prep Courses
- PMBOK® Guide – 7th Edition: The official PMI guide is the primary resource for understanding project management frameworks and methodologies.
- Brain Sensei PMP Exam Prep Course: A unique animated course that makes learning interactive and engaging.
- Head First PMP: A visually engaging book that presents complex topics through graphics and interactive exercises.
- PMP Exam Prep Simplified by Andrew Ramdayal: Breaks down exam concepts into an easy-to-digest format.
Exam Simulators and Question Banks
PMP exam simulators are essential for testing knowledge and improving time management skills under exam conditions. Some highly rated simulators include:
- Brain Sensei’s Unlimited Exam Simulator: Provides over 1,500 realistic PMP practice questions with detailed explanations and a full 6 months of access.
- Whizlabs PMP Exam Simulator: Offers topic-wise questions to strengthen weak areas.
- BrainBOK PMP Practice Exams: Focuses on ITTO-based (Inputs, Tools, Techniques, and Outputs) questions aligned with PMBOK.
- Simplilearn PMP Mock Tests: Features full-length practice tests to assess readiness.
Online Communities and Discussion Forums
Engaging with PMP study groups and online forums can help candidates clarify doubts, share insights, and stay motivated. Some top forums include:
- PMI’s Online Community: Official PMI platform for PMP aspirants.
- Reddit r/pmp: A community of PMP candidates sharing study tips and experiences.
- ProjectManagement.com Discussion Boards: PMI’s dedicated discussion hub.
- LinkedIn PMP Groups: Professional groups for networking and study discussions.
- Brain Sensei’s Facebook Study Group: A community of fellow PMP aspirants, PMP holders and Brain Sensei PMP exam experts
By leveraging these study materials and tools, PMP candidates can enhance their learning experience, boost confidence, and increase their chances of exam success.
Conclusion
Mastering the Process Groups and Knowledge Areas defined in the PMBOK® Guide 7th Edition is essential for any project manager seeking to enhance their skills and ensure project success. The process group and knowledge table provides a structured framework for project execution, ensuring all aspects of a project are addressed systematically.
By leveraging study materials, exam simulators, and practical applications, PMP candidates can reinforce their understanding of these concepts and improve their chances of passing the PMP exam. Additionally, applying these principles in real-world project management enhances efficiency, reduces risks, and ensures stakeholder satisfaction.
For those preparing for the PMP exam or looking to refine their project management approach, using the process group and knowledge table as a reference will be invaluable. The PMBOK® Guide offers a proven methodology that can be adapted across industries, making it a fundamental resource for all project management professionals.
Are you preparing for the PMP exam? Download our free Sample PMP Exam PDF.
Download a Full FREE Sample PMP Exam! Enter your information and get instant access to a downloadable and printable Free PMP Exam PDF with 180 PMP practice questions
To boost your chances of success. Check out Brain Sensei’s PMP Exam Prep resources to take your project management skills to the next level. 99.6% of Brain Sensei students pass their PMP on the first try.